Video hướng dẫn giải
Tính diện tích hình phẳng giới hạn bởi các đường:
LG a
a) \(y={x^2},y =x + 2\);
Phương pháp giải:
Cho hai hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right);\;\;y = g\left( x \right)\) liên tục trên đoạn \(\left[ {a;\;b} \right]\). Gọi \(D\) là hình phẳng được giới hạn bởi đồ thị hai hàm số trên và các đường thẳng \(x = a;\;\;x = b\). Khi đó diện tích của hình phẳng \(D\) được tính bởi công thức: \({S_D} = \int\limits_a^b {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} .\)
Lời giải chi tiết:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị là: \(f(x) = x^2-x -2 =0 \) \(⇔(x+1)(x-2)=0 \) \( ⇔\left[ \begin{array}{l}x + 1=0\\x - 2=0\end{array} \right. \) \( ⇔ \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = - 1\\x = 2\end{array} \right..\)
Diện tích hình phẳng cần tìm là:
\(S=\int_{-1}^{2}\left |x^{2}- x- 2 \right |dx\) \( = \left | \int_{-1}^{2}\left (x^{2}- x- 2 \right ) dx \right |\)
\(=\left |\dfrac{x^{3}}{3}-\dfrac{x^{2}}{2}-2x|_{-1}^{2} \right |\) \(=\left |\dfrac{8}{3}-2-4-(-\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}+2) \right |\) \(=\dfrac{9}{2}\) (đvdt).
LG b
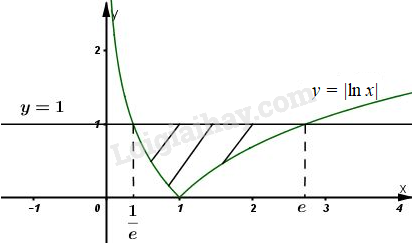
b) \(y = |lnx|, y = 1\);
Lời giải chi tiết:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị là:
\(f(x) = 1 - |\ln x| = 0 ⇔ \ln x = ± 1\) \(⇔\left[ \begin{array}{l}x = e\\x = \dfrac{1}{e}\end{array} \right..\)
Ta có: \(y = |\ln x| = \ln x\) nếu \(\ln x ≥ 0\), tức là \(x ≥ 1\).
hoặc \(y = |\ln x| = - \ln x\) nếu \(\ln x < 0\), tức là \(0 < x < 1\).
Dựa vào đồ thị hàm số vẽ ở hình trên ta có diện tích cần tìm là :
\(S=\int_{\frac{1}{e}}^{e}|1- |\ln x||dx \) \(=\int_{\frac{1}{e}}^{1}(1+\ln x)dx\) \( +\int_{1}^{e}(1-\ln x)dx\)
\(= x|_{\frac{1}{e}}^{1}+\int_{\frac{1}{e}}^{1}\ln xdx +x|_{1}^{e}-\int_{1}^{e}\ln xdx\)
\( = \left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{e}} \right) + \int\limits_{1/e}^1 {\ln xdx} \) \( + \left( {e - 1} \right) - \int\limits_1^e {\ln xdx} \)
\(=-\dfrac{1}{e}+e+\int_{\frac{1}{e}}^{1}\ln x dx-\int_{1}^{e}\ln xdx\)
Tính \(\int {\ln xdx} \) ta có:
Đặt \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}u = \ln x\\dv = dx\end{array} \right. \Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}du = \dfrac{1}{x}dx\\v = x\end{array} \right.\)
Do đó \(∫\ln xdx = x\ln x - ∫dx \) \(= x\ln x – x + C\), thay vào trên ta được:
\(S=e-\dfrac{1}{e}+(x\ln x-x)|_{\frac{1}{e}}^{1}\) \(- (x\ln x-x)|_{1}^{e}\) \( = e - \dfrac{1}{e}\)\( + \left[ {\left( {1\ln 1 - 1} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{e}\ln \dfrac{1}{e} - \dfrac{1}{e}} \right)} \right]\) \( - \left[ {\left( {e\ln e - e} \right) - \left( {1\ln 1 - 1} \right)} \right]\)
\( = e - \dfrac{1}{e}\)\( + \left[ {\left( {0 - 1} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{e}.\left( { - 1} \right) - \dfrac{1}{e}} \right)} \right]\) \( - \left[ {\left( {e.1 - e} \right) - \left( {0 - 1} \right)} \right]\)
\( = e - \dfrac{1}{e} + \left( { - 1 + \dfrac{2}{e}} \right) - \left( {0 + 1} \right)\) \( = e - \dfrac{1}{e} - 1 + \dfrac{2}{e} - 1\)
\(=e+\dfrac{1}{e}-2\) (đvdt).
LG c
c) \(y = {\left( x-6 \right)}^2,y = 6x-{x^2}\)
Lời giải chi tiết:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị là:
\(f\left( x \right) =6x-{x^2}-{\left( {x -6} \right)^2} \) \(= - 2({x^2}-9x+ 18)=0\)
\( \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 9x + 18 = 0\) \(⇔ (x-3)(x-6)=0\) \(⇔ \left[ \begin{array}{l}x - 3=0\\x - 6=0\end{array} \right.\) \(⇔\left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 3\\x = 6\end{array} \right..\)
Diện tích cần tìm là:
\(S=\int_{3}^{6}|-2(x^{2}-9x+18)|dx\) \(=|2\int_{3}^{6}(x^{2}-9x+18)dx|\)
\(=\left |2(\dfrac{x^{3}}{3}-\dfrac{9}{2}x^{2}+18x)|_{3}^{6} \right | \)
\( = |2\left( {\dfrac{{{6^3}}}{3} - \dfrac{9}{2}{{.6}^2} + 18.6} \right)\) \( - 2\left( {\dfrac{{{3^3}}}{3} - \dfrac{9}{2}{{.3}^2} + 18.3} \right)|\)
\( =|36-45|=9 \, \, (đvdt)\).
soanvan.me